本文作者:石油醚
概要
Thorsten Bach (1965年生于路德维希港/莱茵),德国科学院院士,Bavarian科学与人文学院院士,慕尼黑工业大学化学系教授,有机化学系主任,有机化学家,课题组主页:https://www.department.ch.tum.de/en/oc1/home/
经历
- 1989年之前 海德堡大学和南加州大学学习化学
- 1989年-1991年 马尔堡大学获得博士学位(Prof. M.T. Reetz)
- 1991年-1992年 哈佛大学博士后(Prof. D.A.Evans)
- 1992年-1996年 明斯特大学讲师
- 1997年-2000年 马尔堡大学担任教学和研究职务
- 2000年-至今 慕尼黑工业大学化学系教授
- 2006年-至今 德国科学院院士
- 2009年-至今 巴伐利亚科学与人文学院院士
获奖经历
- ADUC Jahrespreis für Habilitanden 1995
- Dozentenstipendium des FCI 1997
- AstraZeneca Research Award 2001
- Novartis European Young Investigator Award 2003
- Degussa Award for Chirality in Chemistry 2006
- ERC Advanced Grant 2015
- JSPS Fellowship 2016
- Horst Pracejus Preis 2017
- Emil-Fischer-Medaille 2018
- Novartis Lectureship 2003
- Boehringer Ingelheim Lectureship 2009
- Honda-Fujishima Lectureship 2014
- Jerome A. Berson Lecture 2016
- Victor J. Chambers Lectureship 2019
研究方向
Bach教授研究重点是有机合成化学,尤其是立体选择性转化。 他开发了多种新方法,其中包括光化学过程,新催化反应(C-H活化,催化氧化,路易斯酸催化)的研究和使用以及复杂天然产物的全合成。
1. 天然产物全合成
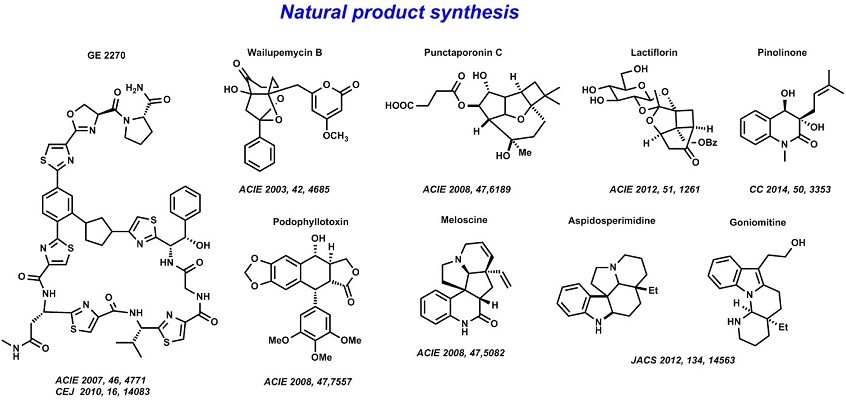
Bach教授中全合成的目标的选择基于结构独特,合适的新方法学和生物活性等方面 。目前,小组已经完成了一些天然产物的首次全合成以及证实了它们的组成和结构。Bach教授开发新的合成方法并应用于wailupemycin B1, punctaporonin C2, lactiflorin3, and pinolinone4的全合成中(Fig.1)。如1)光介导的对映选择性催化成为meloscine5全合成中关键步骤;2)吲哚C2位置的C-H活化被用于aspidosperma alkaloids meloscine6的合成;3)对碳离子的非对映选择性反应的兴趣造就了podophyllotoxin.7的简短合成。天然产物的生物活性是驱使化学家合成它们的动机之一。在这方面,Bach教授致力于合成抗击癌症和抵抗感染的化合物。如GE-因子8和支链淀粉菌素的合成时涉及细菌延伸因子EF-Tu。通过后期研究和修饰,成功的阐明了的EF-Tu抑制剂的作用方式,并为vioprolide的生物合成9途径做出了贡献。除致力于天然产物全合成的之外,还致力于药物化学新支架的制备10和用于生物学研究新探针的开发11 。
Figure 1 天然产物全合成
2. 催化方法
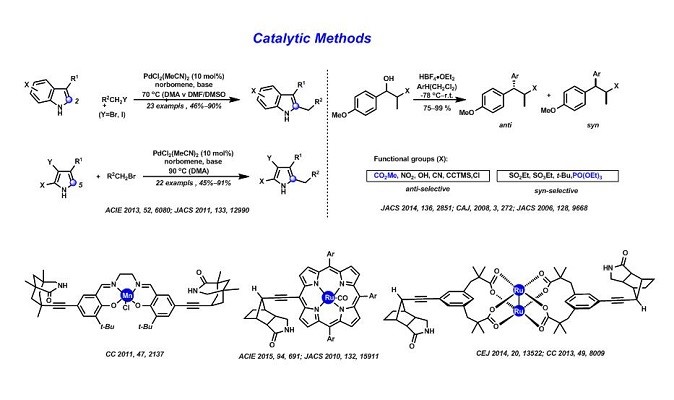
对杂环化合物合成的兴趣导致区域选择性交叉偶联反应的发展并广泛的应用。近年来,Bach小组的兴趣已转向通过C-H活化直接在杂环上形成C-C键12,实现了吲哚和吡咯的烷基化和噻吩的芳基化13,14。在新的催化方法上Bach教授主要涉及1)使用FeCl3,AuCl3,Bi(Otf)315作为催化剂解决了游离碳正离子的分子间反应中的面部非对映选择性16,而其主要受阳离子在ɑ-位的立体中心取代基的尺寸大小的影响;2)氢键催化领域初步的工作主要是为光反应寻找合适的对映选择性催化剂。而目前,氢键催化方面主要集中于对映和区域选择性过渡金属催化方面。基于此,设计并合成通过氢键与底物结合的位点,并且还能够连接具有催化活性的过渡金属(Mn,Ru或Rh)的模板催化剂。通过使用不同过渡金属的催化剂去催化不同的反应(其中Ru基催化剂17,18可以使喹诺酮基烯烃进行选择性环氧化反应,Rh基催化能19够解决对映选择性胺化和叠氮化的问题,Mn基催化剂20,21能够发生定点和高度对映选择性的氧化反应。),结过证明了氢键是区域选择性和对映选择性的原因。目前,基于上述新的反应策略,我们在烯丙基与烯丙基阳离子,C-H胺化22和吡咯合成23等方面继续研究。( Fig.2 )
Figure 2 催化新方法
3. 光催化
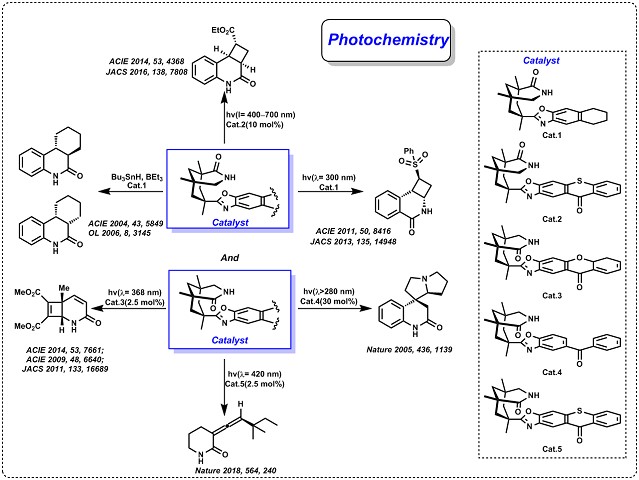
基于Kemp 三羧酸获得的1,5,7-三甲基-3-氮杂双环[3.3.1]壬烷-2骨架,Bach教授开发了用于光化学和自由基反应的手性催化剂24,25,在过去十年中证明了这类手性催化剂的多功能性以及自由基反应中显示出一些对映选择性的催化活性( Fig.3 )。 近年来,它已成功用于:1)分子内和分子间[2+2] 环加成构建异喹诺酮骨架26,27;2)恶唑主链修饰后,可以将催化剂开发为对映选择性催化剂。该催化剂通过电子转移或能量转移起作用,在氨乙基喹诺酮的对映选择性光氧化还原环化反应28和呫吨酮的 [2 + 2] 对映选择性光催化环化反应29-31;3)可见光或阳光条件下,手性硫杂蒽酮能使喹诺酮类化合物32,33进行分子间和分子内[2+2]光环加成反应,该类催化剂最显著作用是能使联烯类化合物的去外消旋化34。
Figure 3 手性光催化剂的设计
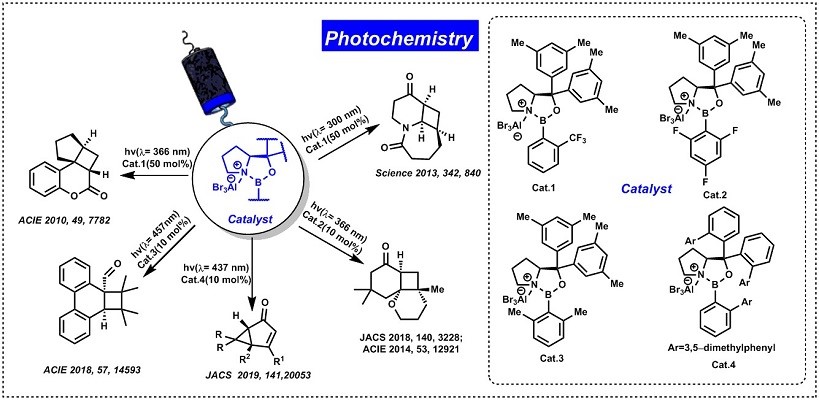
路易斯酸催化是实现对映选择性光化学反应的一种方法35,36。如在2013年,Bach教授研究发现路易斯酸催化不仅限于香豆素类[2 + 2]的对映选择性光环加成反应37,还可以应用于烯酮[2 + 2]的对映选择性光环加成反应。Bach教授在路易斯催化光环加成方面的成果主要是:1)与香豆素类不同,烯酮在366 nm的波长处经历了未催化的[2+2]环加成反应35,38,39。很明显,烯酮与香豆素类化合物在光环加成反应的作用形式不同,并且其路易斯酸催化烯酮[2 + 2] 的对映选择性光环加成的似乎相对普遍,不仅应用于二氢吡啶酮,而且最近也应用于2-环己烯酮底物;2)菲-9-甲醛的[2+2]光环加成的例子40,成功的证明了未与路易斯酸及其结合路易斯酸络合物的底物在UV / Vis光谱的长波长区域中不显示出重叠,就可以克服高催化剂负载的缺点。
Figure 4 路易酸催化光环加成
其他
2015年的Angew中Thorsten Bach教授提出
“ More Chemistry with Light! More Light in Chemistry! ”
参考文献
- [1] Kirsch, S. & Bach, T.Total Synthesis of (+)-Wailupemycin B. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. (2003) 42, 4685-4687, doi:10.1002/anie.200351455.
- [2] Fleck, M. & Bach, T.Total Synthesis of the Tetracyclic Sesquiterpene (±)-Punctaporonin C. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. (2008) 47, 6189-6191, doi:10.1002/anie.200801534.
- [3] Lu, P. & Bach, T.Total Synthesis of (+)-Lactiflorin by an Intramolecular [2+2] Photocycloaddition. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. (2012) 51, 1261-1264, doi:10.1002/anie.201106889.
- [4] Mayr, F., Wiegand, C. & Bach, T.Enantioselective, intermolecular [2+2] photocycloaddition reactions of 3-acetoxyquinolone: total synthesis of (−)-pinolinone. Chem. Commun. (2014) 50, 3353-3355, doi:10.1039/C3CC49469A.
- [5] Selig, P. & Bach, T.Enantioselective Total Synthesis of the Melodinus Alkaloid (+)-Meloscine. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. (2008) 47, 5082-5084, doi:10.1002/anie.200800693.
- [6] Jiao, L., Herdtweck, E. & Bach, T.Pd(II)-Catalyzed Regioselective 2-Alkylation of Indoles via a Norbornene-Mediated C–H Activation: Mechanism and Applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. (2012) 134, 14563-14572, doi:10.1021/ja3058138.
- [7] Stadler, D. & Bach, T.Concise Stereoselective Synthesis of (−)-Podophyllotoxin by an Intermolecular Iron(III)-Catalyzed Friedel–Crafts Alkylation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. (2008) 47, 7557-7559, doi:10.1002/anie.200802611.
- [8] Müller, H. M., Delgado, O. & Bach, T.Total Synthesis of the Thiazolyl Peptide GE2270 A. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. (2007) 46, 4771-4774, doi:10.1002/anie.200700684.
- [9] Yan, F. et al.Biosynthesis and Heterologous Production of Vioprolides: Rational Biosynthetic Engineering and Unprecedented 4-Methylazetidinecarboxylic Acid Formation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. (2018) 57, 8754-8759, doi:10.1002/anie.201802479.
- [10] Fort, D. A., Woltering, T. J., Nettekoven, M., Knust, H. & Bach, T.Synthesis of Fluorinated Tricyclic Scaffolds by Intramolecular [2+2] Photocycloaddition Reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. (2012) 51, 10169-10172, doi:10.1002/anie.201204080.
- [11] Roberts, S. et al.Calcium Sensor for Photoacoustic Imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. (2018) 140, 2718-2721, doi:10.1021/jacs.7b03064.
- [12] Schröter, S., Stock, C. & Bach, T.Regioselective cross-coupling reactions of multiple halogenated nitrogen-, oxygen-, and sulfur-containing heterocycles. Tetrahedron (2005) 61, 2245-2267, doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2004.11.074.
- [13] Jiao, L. & Bach, T.Palladium-Catalyzed Direct C-H Alkylation of Electron-Deficient Pyrrole Derivatives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. (2013) 52, 6080-6083, doi:10.1002/anie.201301154.
- [14] Jiao, L. & Bach, T.Palladium-Catalyzed Direct 2-Alkylation of Indoles by Norbornene-Mediated Regioselective Cascade C–H Activation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. (2011) 133, 12990-12993, doi:10.1021/ja2055066.
- [15] Nitsch, D. et al.Chiral Propargylic Cations as Intermediates in SN1-Type Reactions: Substitution Pattern, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Studies, and Origin of the Diastereoselectivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. (2014) 136, 2851-2857, doi:10.1021/ja411772n.
- [16] Mühlthau, F. et al.Chiral α-Branched Benzylic Carbocations: Diastereoselective Intermolecular Reactions with Arene Nucleophiles and NMR Spectroscopic Studies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. (2006) 128, 9668-9675, doi:10.1021/ja062102g.
- [17] Fackler, P., Berthold, C., Voss, F. & Bach, T.Hydrogen-Bond-Mediated Enantio- and Regioselectivity in a Ru-Catalyzed Epoxidation Reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. (2010) 132, 15911-15913, doi:10.1021/ja107601k.
- [18] Frost, J. R., Huber, S. M., Breitenlechner, S., Bannwarth, C. & Bach, T.Enantiotopos-Selective CH Oxygenation Catalyzed by a Supramolecular Ruthenium Complex. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. (2015) 54, 691-695, doi:10.1002/anie.201409224.
- [19] Höke, T., Herdtweck, E. & Bach, T.Hydrogen-bond mediated regio- and enantioselectivity in a C–H amination reaction catalysed by a supramolecular Rh(ii) complex. Chem. Commun. (2013) 49, 8009-8011, doi:10.1039/C3CC44197K.
- [20] Voss, F., Herdtweck, E. & Bach, T.Hydrogen bond induced enantioselectivity in Mn(salen)-catalysed sulfoxidaton reactions. Chem. Commun. (2011) 47, 2137-2139, doi:10.1039/C0CC04636A.
- [21] Burg, F., Gicquel, M., Breitenlechner, S., Pöthig, A. & Bach, T.Site- and Enantioselective C−H Oxygenation Catalyzed by a Chiral Manganese Porphyrin Complex with a Remote Binding Site. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. (2018) 57, 2953-2957, doi:10.1002/anie.201712340.
- [22] Wippich, J., Truchan, N. & Bach, T.Rhodium-Catalyzed N-tert-Butoxycarbonyl (Boc) Amination by Directed CH Bond Activation. Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis (2016) 358, 2083-2087, doi:10.1002/adsc.201600410.
- [23] Wiest, J. M. & Bach, T.A Route to 2-Substituted 3-Cyanopyrroles: Synthesis of Danaidal and Suffrutine A. J. Org. Chem. (2016) 81, 6149-6156, doi:10.1021/acs.joc.6b01298.
- [24] Aechtner, T., Dressel, M. & Bach, T.Hydrogen Bond Mediated Enantioselectivity of Radical Reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. (2004) 43, 5849-5851, doi:10.1002/anie.200461222.
- [25] Dressel, M. & Bach, T.Chirality Multiplication and Efficient Chirality Transfer in exo- and endo-Radical Cyclization Reactions of 4-(4‘-Iodobutyl)quinolones. Org. Lett. (2006) 8, 3145-3147, doi:10.1021/ol061194b.
- [26] Austin, K. A. B., Herdtweck, E. & Bach, T.Intramolecular [2+2] Photocycloaddition of Substituted Isoquinolones: Enantioselectivity and Kinetic Resolution Induced by a Chiral Template. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. (2011) 50, 8416-8419, doi:10.1002/anie.201103051.
- [27] Coote, S. C. & Bach, T.Enantioselective Intermolecular [2+2] Photocycloadditions of Isoquinolone Mediated by a Chiral Hydrogen-Bonding Template. J. Am. Chem. Soc. (2013) 135, 14948-14951, doi:10.1021/ja408167r.
- [28] Bauer, A., Westkämper, F., Grimme, S. & Bach, T.Catalytic enantioselective reactions driven by photoinduced electron transfer. Nature (2005) 436, 1139-1140, doi:10.1038/nature03955.
- [29] Maturi, M. M. & Bach, T.Enantioselective Catalysis of the Intermolecular [2+2] Photocycloaddition between 2-Pyridones and Acetylenedicarboxylates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. (2014) 53, 7661-7664, doi:10.1002/anie.201403885.
- [30] Müller, C., Bauer, A. & Bach, T.Light-Driven Enantioselective Organocatalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. (2009) 48, 6640-6642, doi:10.1002/anie.200901603.
- [31] Müller, C. et al.Enantioselective Intramolecular [2 + 2]-Photocycloaddition Reactions of 4-Substituted Quinolones Catalyzed by a Chiral Sensitizer with a Hydrogen-Bonding Motif. J. Am. Chem. Soc. (2011) 133, 16689-16697, doi:10.1021/ja207480q.
- [32] Alonso, R. & Bach, T.A Chiral Thioxanthone as an Organocatalyst for Enantioselective [2+2] Photocycloaddition Reactions Induced by Visible Light. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. (2014) 53, 4368-4371, doi:10.1002/anie.201310997.
- [33] Tröster, A., Alonso, R., Bauer, A. & Bach, T.Enantioselective Intermolecular [2 + 2] Photocycloaddition Reactions of 2(1H)-Quinolones Induced by Visible Light Irradiation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. (2016) 138, 7808-7811, doi:10.1021/jacs.6b03221.
- [34] Hölzl-Hobmeier, A. et al.Catalytic deracemization of chiral allenes by sensitized excitation with visible light. Nature (2018) 564, 240-243, doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0755-1.
- [35] Brimioulle, R. & Bach, T.Enantioselective Lewis Acid Catalysis of Intramolecular Enone [2+2] Photocycloaddition Reactions. Science. (2013) 342, 840-843, doi:10.1126/science.1244809
- [36] Leverenz, M., Merten, C., Dreuw, A. & Bach, T.Lewis Acid Catalyzed Enantioselective Photochemical Rearrangements on the Singlet Potential Energy Surface. J. Am. Chem. Soc. (2019) 141, 20053-20057, doi:10.1021/jacs.9b12068.
- [37] Guo, H., Herdtweck, E. & Bach, T.Enantioselective Lewis Acid Catalysis in Intramolecular [2+2] Photocycloaddition Reactions of Coumarins. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. (2010) 49, 7782-7785, doi:10.1002/anie.201003619.
- [38] Poplata, S. & Bach, T.Enantioselective Intermolecular [2+2] Photocycloaddition Reaction of Cyclic Enones and Its Application in a Synthesis of (−)-Grandisol. J. Am. Chem. Soc. (2018) 140, 3228-3231, doi:10.1021/jacs.8b01011.
- [39] Brimioulle, R. & Bach, T.[2+2] Photocycloaddition of 3-Alkenyloxy-2-cycloalkenones: Enantioselective Lewis Acid Catalysis and Ring Expansion. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. (2014) 53, 12921-12924, doi:10.1002/anie.201407832.
- [40] Stegbauer, S., Jandl, C. & Bach, T.Enantioselective Lewis Acid Catalyzed ortho Photocycloaddition of Olefins to Phenanthrene-9-carboxaldehydes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. (2018) 57, 14593-14596, doi:10.1002/anie.201808919.
本文版权属于 Chem-Station化学空间, 欢迎点击按钮分享,未经许可,谢绝转载!



























No comments yet.